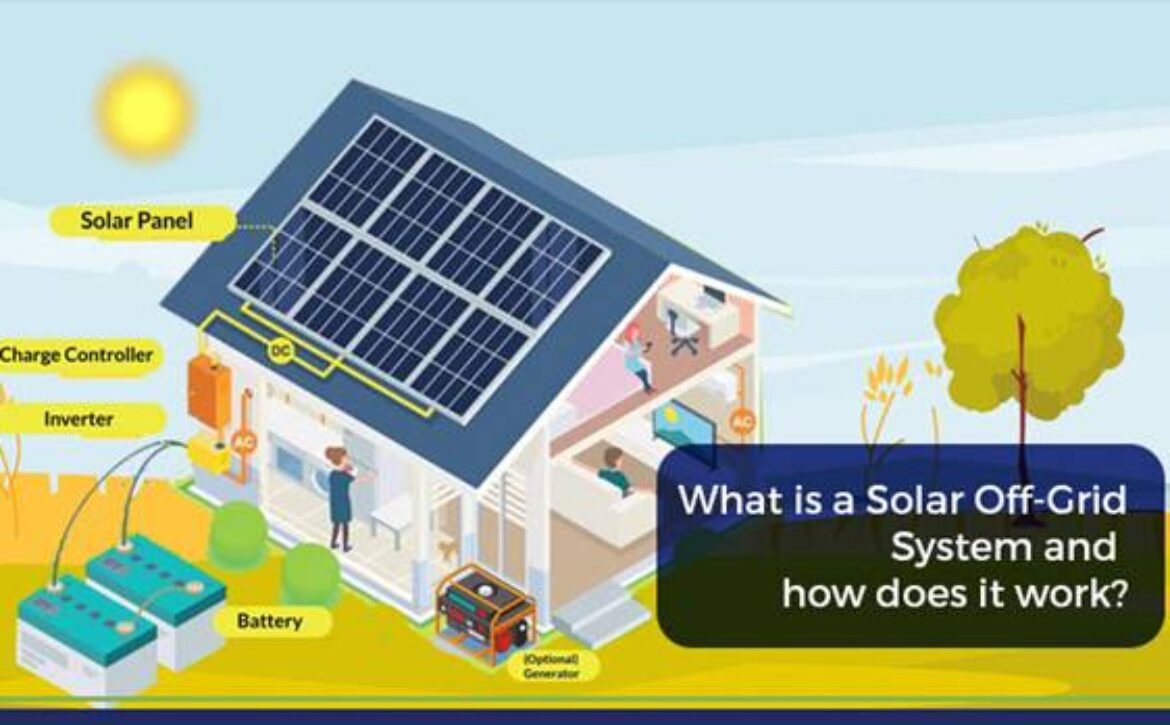
List of Top 10 Solar Panel Manufacturers in India
The solar energy sector has huge potential to keep the industrial wheels running and power homes with free electricity. We however still need to develop the required infrastructure to provide the best quality solar panels and other products in the required quantity in the market. We have carefully prepared a list of the top 10 Solar panel manufacturers in India that are providing the best quality solar panels.
List of Top 10 Solar Panel Manufacturers in India 2023
Here you will get the list of top 10 solar panel manufacturers in India 2023 as big names in the solar energy sector. They are continuously offering the best quality solar panels to actively contribute to a clean environment and free energy solutions. Have a look

1. Tata Power Solar

Tata Solar is serving in the industry for over 3 decades. It provides solar panels to generate clean energy for residences, commercial & industrial and institutions. Tata Power Solar module manufacturing lines have an in-house production capacity of 635MW for modules and 500MW of cell manufacturing lines with a capacity of 528MW. It also offers comprehensive green energy solutions for rural and urban areas like turnkey, EPC, and O&M solutions for various business segments like utility-scale projects, solar rooftops, and solar pump systems.
2. Adani Solar

Adani Solar was incorporated in 2016. This solar panel manufacturer in India has a 4 GW manufacturing capacity. The company offers mono facial & bifacial modules (in PERC Technology) which help to tap solar energy. Currently, Adani Solar is creating an ecosystem for 10 GW Solar PV Manufacturing in India.
3. Servotech Renewable Power System Ltd.

Servotech is an award-winning solar panel company in India that significantly contributes to clean energy generation with meticulously engineered solar panels. This frontline solar products manufacturer in India boasts a wide experience of over 18 years and maintains an extensive range of highly beneficial solar energy products like Solar Inverters, Solar Batteries, Solar Panels, etc. Servotech offers a complete range of solar solutions including Solar EPC Services.
Servotech Renewable Power System Ltd. has a wide profile of projects and successfully delivered various solar power projects to many state governments, state nodal agencies, fuel retailers, oil refineries, etc. Servotech Power Systems Limited also manufactured India’s first portable solar rooftop system PV Ports which was installed at various famous and unique public places in India.
Servotech has also developed a solar performance monitoring & controlling device ComPort in association with GIZ. The Servotech R&D team has also developed a Solar-powered Carport. Besides, Servotech maintains a pan India presence with over 1000 dealers and continuously increases its channel partner distribution network.
4. Waaree Energies Ltd

Waaree Energies Ltd. was founded in 1989. Since its beginning, it has covered a long journey of more than 3 decades and now comprehends a manufacturing capacity of over 12GW. Waaree Energies is the largest solar panel manufacturer in India and maintains a noticeable position in the solar energy sector while having a presence in over 380 locations in India & 20 foreign nations.

Read more: Can Your House Run on a 5kW Solar System?
5. Vikram Solar

Vikram Solar was founded in 2006. A presence in the solar energy sector of more than 32 countries, experience in the installation of 1.42 GW projects in India, and annual manufacturing capacity of 3.5 GW modules make Vikram Solar a competent brand in the solar energy industry. This solar panel manufacturer is ambitiously working to meet India’s green energy goal of 500 GW by 2030. So far, Vikram Solar has commissioned more than 300 projects at multiple locations.
6. Goldi Solar

Gujarat-based Goldi Solar was started in 2011. It offers solar energy products in the domestic market as well as in 20 other countries. Goldi Solar has achieved a record growth from 10 MW to 500 MW manufacturing capacity in a span of just 10 years. Goldi Solar has annual manufacturing capabilities of 2.5 GW and currently planning to add another 2000 MW by the end of 2023.

7. Saatvik Green Energy Pvt. Ltd.

Saatvik Green Energy Pvt. Ltd. started its journey in the solar sector in 2015 from Haryana. It actively contributes to the solar energy sector with an annual production capacity of 1 GW. This solar panel manufacturer has its manufacturing plant in Ambala (Haryana) and soon going to set up another one with a capacity of 1.2 GW at Gandhidham, Gujarat.
8. Renewsys India

Since beginning in 2011, Renewsys India has covered a long journey of 12 years and moving ahead with a total installed module manufacturing capacity of 2.75 GW. It offers a long range of solar products including Solar panels, PV Cells, PV Encapsulants – EVA & POE, and PV back sheets. RenewSys supplies solar products to over 40 countries. This solar panel manufacturer has three manufacturing plants in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Patalganga.
9. Loom Solar Pvt. Ltd

Loom Solar entered the solar panel manufacturing industry of India in 2018 from Faridabad, Haryana. Currently, it offers solar panels to generate clean energy as well as maintains a channel sales network with over 3500 resellers in over 500 districts of Indian states. The annual manufacturing capacity of Loom Solar stands at 100 MW.
10. Patanjali

With an existing capacity of 72 MW Patanjali is another solar panel manufacturer in the solar energy sector of India. Currently, Patanjali is ambitiously trying to increase operational capacity up to 500 MW by the end of 2023.
Conclusion
Easy availability of solar products in the market can appropriately solve the problems of shortage of power supply and keep the environment clean against highly polluting electricity-generating procedures. The solar industry also needs to create a viable framework to benefit more and more people.
Read more: How Much Savings You Can Make with a Solar System


 Get Quote
Get Quote